Welcome to our comprehensive guide to tracking subscription billing metrics, explicitly tailored for subscription merchants like you, who offer subscription products or services to your customers. Understanding and monitoring the key metrics impacting your subscription business can improve customer satisfaction, reduce refund rates, and optimize revenue.
In this guide, we will cover seven essential billing metrics that can impact the success of your business. We will explain each metric, how to calculate it, and provide actionable strategies for improving it. These metrics include:
- Payment Collection Rate
- Payment Decline Rate
- Refund Rate
- Chargeback Rate
- Fraud Detection Rate
- Account Updater Rate
By understanding the above metrics, you can identify areas for improvement that can impact the most important subscription metrics we outlined previously. These metrics are significant leading indicators of your business’s overall success and profitability.
To dive deeper into the world of subscription billing metrics, we will explore the critical role that data segmentation plays in optimizing your subscription billing performance. By breaking down large sets of data into smaller, more manageable groups based on specific characteristics or attributes, you can gain valuable insights into areas of your business that may require improvement.
So, let’s get started on optimizing your subscription business performance by tracking your billing metrics and leveraging data segmentation to achieve your goals!
Payment Collection Rate
Definition of Payment Collection Rate
Payment collection rate is the rate at which recurring payments for a subscription business are successfully collected. It is a metric that tracks how many of your recurring payments are successfully processed.
Importance of Tracking Payment Collection Rate
Tracking the payment collection rate is crucial for subscription businesses as it provides insight into the health of the revenue stream. High payment collection rates indicate that you are consistently collecting payments, while low payment collection rates may demonstrate issues with payment processing, customer churn, or fraud.
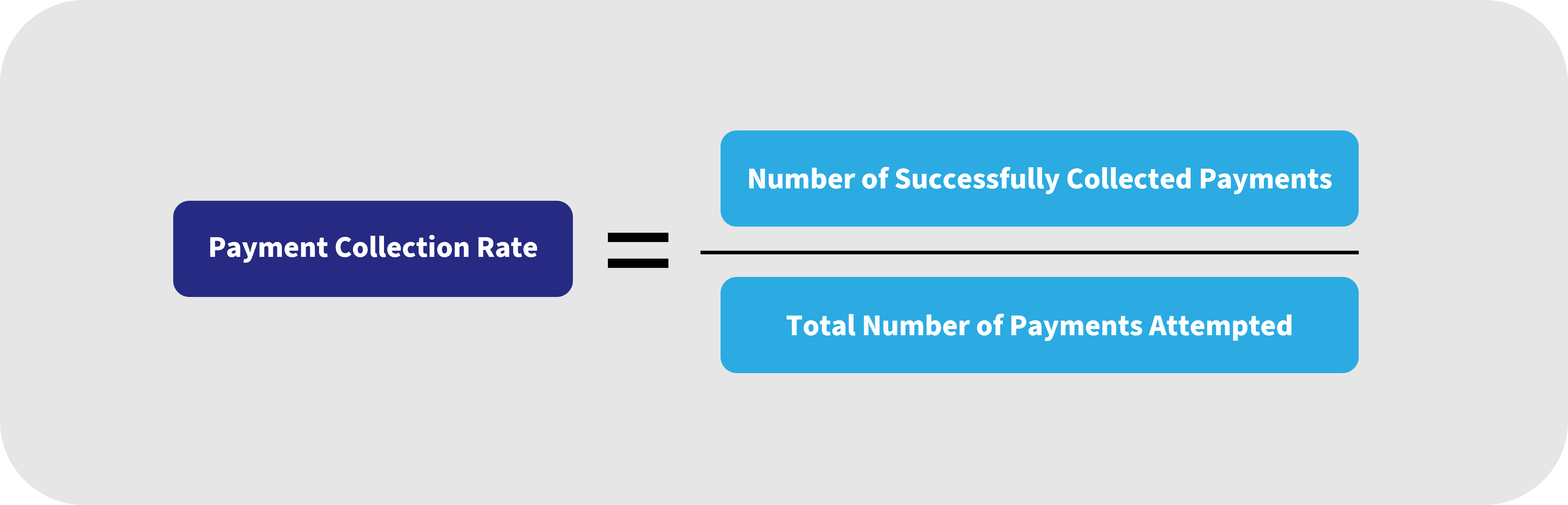
How to Calculate Payment Collection Rate
Payment collection rate is calculated by dividing the number of successfully collected payments by the total number of payments attempted.
Strategies for Improving Payment Collection Rate
- Optimize Payment Processing: Ensure that the payment processing system is dependable and optimized to minimize failures.
- Monitor and Optimize Retry Logic: Analyze failed transactions and adjust the number and timing of retry attempts. Consider implementing automated retry logic and personalizing the retry process for individual customers and transactions.
- Offer Multiple Payment Options: Offer customers various payment options, such as credit cards, PayPal, or direct debits, to minimize the risk of payment failures and increase the likelihood of successful payments.
- Improve Customer Communication: Regularly communicate with customers about their payment status and inform them about upcoming payment due dates to reduce the likelihood of failed payments.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Payment Collection Rate
- Customer: Track payment collection rates by customer segments to identify patterns or issues specific to certain groups of customers and develop targeted strategies to improve Payment Collection Rates.
- Payment Method: Track payment collection rates by payment method to understand which approaches have higher or lower success rates.
- Subscription Plan: Track payment collection rates by subscription plan to identify any differences in success rates between different plans.
- Time-Based: Track payment collection rates over time to identify any trends or changes in success rates.
By segmenting your data, you can better identify which customer groups have the highest or lowest payment collection rates and the reasons behind them. This information will guide you in developing strategies for improving payment collection rates. Additionally, data segmentation can help you identify issues with specific payment channels or providers and make informed decisions about which payment methods to prioritize or discontinue.
Payment Decline Rate
Definition of Payment Decline Rate
The payment decline rate refers to the percentage of automated billing attempts that fail to be collected from the customer’s payment method. In a subscription-based business, it is essential to have a low payment decline rate to ensure the stability of revenue streams.
Importance of Tracking Payment Decline Rate
Tracking payment decline rate is crucial as it helps businesses identify and address potential issues with their billing systems, such as outdated payment information or insufficient funds. The rate is also an essential metric for evaluating the effectiveness of strategies to reduce payment declines and improve payment collection rates.
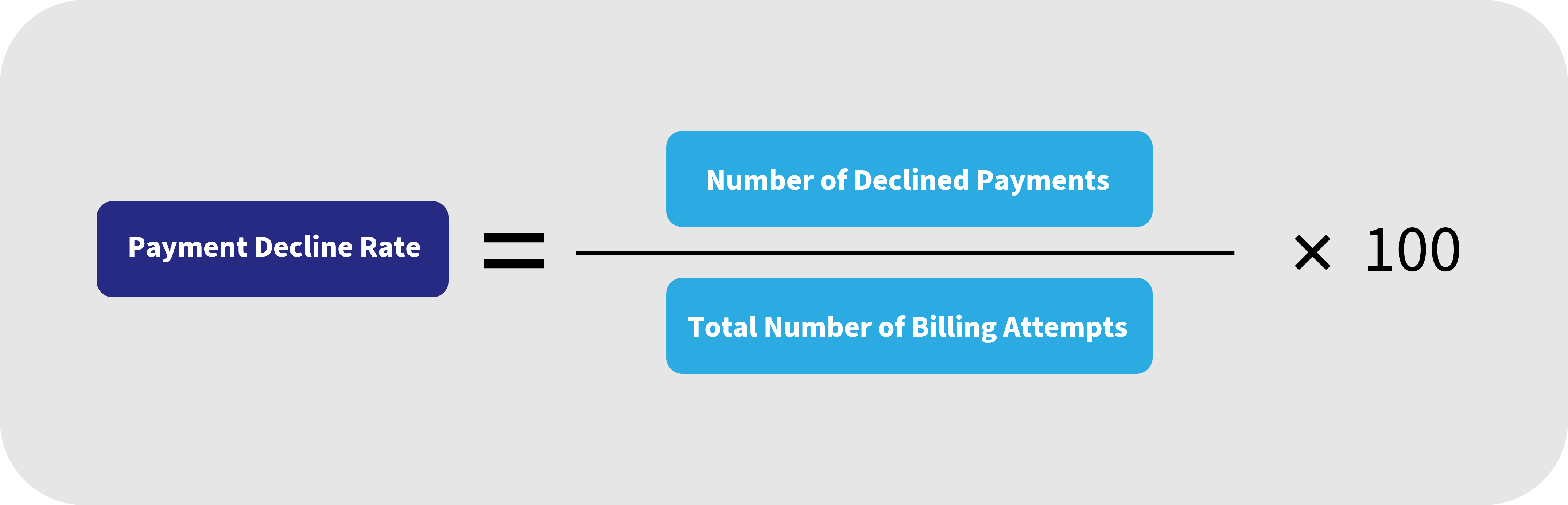
How to Calculate Payment Decline Rate
The payment decline rate is calculated by dividing the number of declined payments by the total number of billing attempts.
Strategies for Reducing Payment Decline Rate
- Keep Payment Information Up-to-date: Ensuring that customer payment information is accurate and up-to-date is vital to reduce payment declines. Consider sending reminders to customers to update their payment information if you suspect it may be outdated.
- Offer Multiple Payment Options: Offer customers multiple payment options to accommodate their preferences, such as offering multiple credit card options, ACH, and alternative payment methods like PayPal or other region-specific payment methods.
- Monitor Decline Trends and Implement Strategies: Monitor payment declines and identify any trends or patterns related to specific days of the week, payment methods, or payment channels. Implement strategies to address these trends and improve payment success rates.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Payment Decline Rate
- Payment Method: Segment by payment method, such as credit card or ACH, to understand payment decline patterns specific to each payment method and identify any issues or trends.
- Subscription Plan: Segment by type of subscription plan to identify any correlation between payment declines and the plan’s cost.
- Billing Cycle/Frequency: To understand if payment declines are more common for monthly or annual subscribers, separate the data by billing cycle or frequency.
- Bank Identification Number (BIN) Range: Segmenting by BIN range helps to identify trends and patterns in payment declines across different banks and payment providers. This can also help you identify any potential red flags or high-risk BINs, allowing you to address any potential issues proactively.
Data segmentation is essential for the payment decline rate as it helps you identify trends and patterns that may not be apparent when looking at the data as a whole. By segmenting the data, you can identify specific customer groups, payment channels, or payment methods that may have a higher decline rate and implement a strategy to improve.
Refund Rate
Definition of Refund Rate
The refund rate refers to the percentage of transactions that result in a customer receiving a refund. You need to track this metric because it provides insight into customer satisfaction, product quality, and return policies.
Importance of Tracking Refund Rate
Tracking the refund rate is critical for understanding the reasons behind customer refunds and identifying areas for improvement. High refund rates may indicate potential issues with product quality, customer service, return policy, or other issues that may cause dissatisfaction or misunderstanding. By monitoring this metric regularly, you can make changes to improve customer satisfaction, reduce refund rates, and increase revenue.
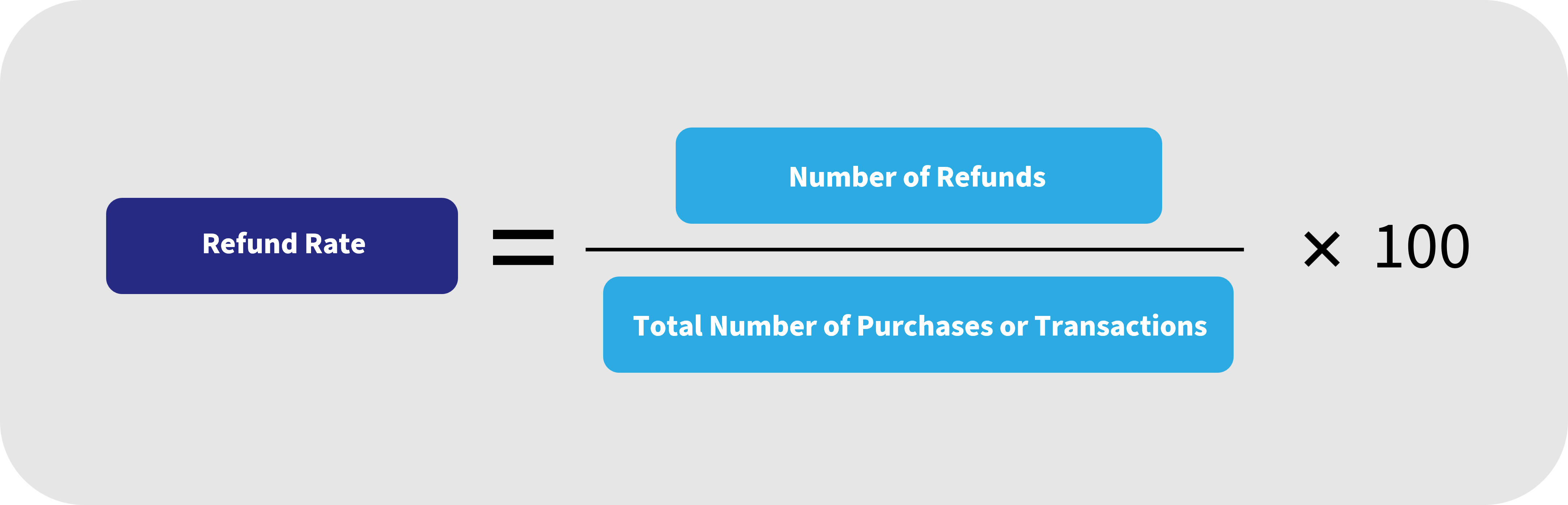
How to Calculate Refund Rate
The refund rate can be calculated by dividing the number of refunds issued by the total number of purchases or transactions, expressed as a percentage.
Strategies for Reducing Refund Rate
- Provide Excellent Service: Provide quick and practical support to resolve customer concerns and prevent refunds.
- Improve Product Quality and Descriptions: Ensure that your product or service meets customer expectations, and the description of each should accurately explain its capabilities.
- Offer Incentives to Reduce Returns: Offer incentives, such as discounts on future purchases, to encourage customers to keep the product instead of returning it and requesting a refund.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Refund Rate
- Customer Demographics: Analyze refund rates based on customer demographics, such as age, gender, location, etc…, to identify patterns.
- Product Categories: Analyze refund rates by product category to understand which products are more likely to be returned.
- Purchase or Marketing Channel: Analyze refund rates based on the purchase channel, whether online or in-app, or by marketing channel, social, organic, or affiliates, to determine any differences.
- Time of Year: Analyze refund rates by season to understand if there are any seasonal trends in refunds.
You can optimize your subscription business, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce return rates by tracking your refund rate and using these actionable insights and data segmentation considerations.
Chargeback Rate
Definition of Chargeback Rate
Chargeback rate is a critical metric for subscription-based businesses as it represents the percentage of transactions that result in a chargeback. A chargeback occurs when a cardholder disputes a charge on their credit card, and the issuing bank reverses the transaction, refunding the cardholder and debiting the merchant’s account.
Importance of Tracking Chargeback Rate
Tracking chargeback rates can provide valuable insight into your business’s performance, customer satisfaction levels, and identify areas for improvement. A high chargeback rate can indicate product or service quality issues, fraud prevention efforts, and other factors. It may also cause increased costs and penalties and harm your reputation as a merchant.
You should monitor and manage your chargeback rates to ensure compliance and avoid penalties and increased costs. The four major card networks (Visa, Mastercard, Discover, and American Express) have chargeback rate thresholds to ensure merchants provide high-quality products and services and take steps to prevent fraud. Each network has its own calculation method to determine the threshold, and these calculations may change over time.
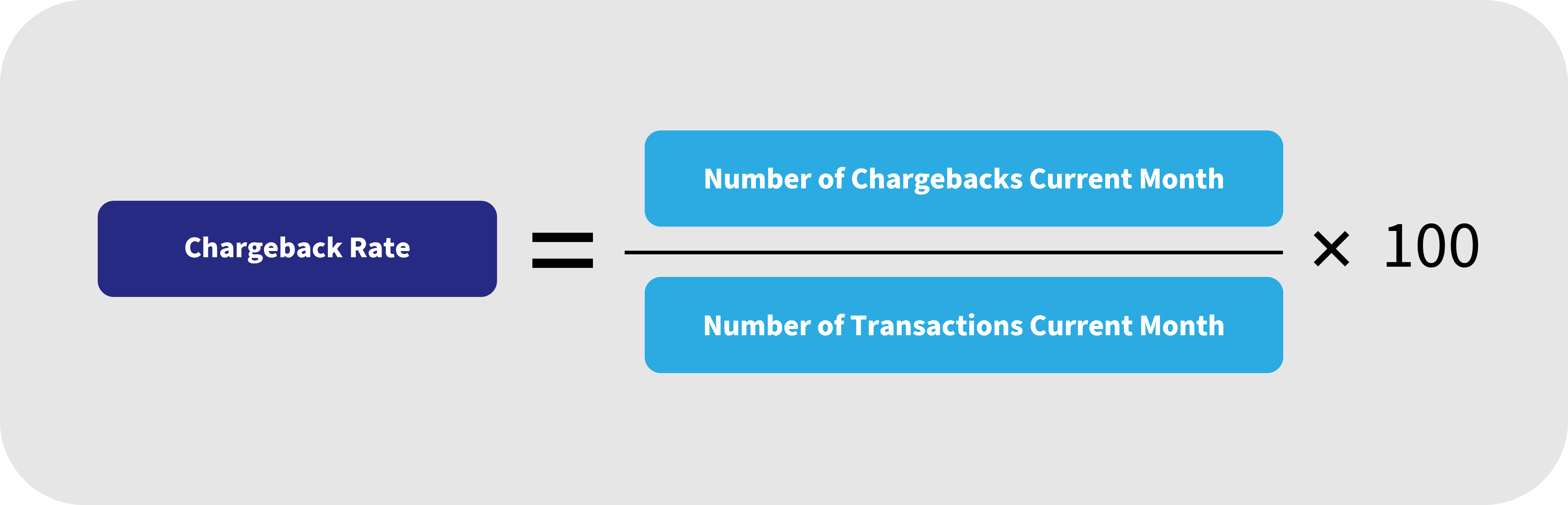
How to Calculate Chargeback Rate
Calculating your Chargeback Rate involves multiple calculations by card network thresholds, but it is important to normalize and track the metric consistently across card networks for trending purposes. To calculate your Chargeback Rate, divide the number of monthly chargebacks by the total number of transactions processed in the same month and multiply by 100.
Strategies for Reducing Chargeback Rate
- Improve Customer Experience: Offer exceptional customer service and make it easy for customers to contact you with concerns or issues. This can include offering multiple channels for customer support, such as phone, email, or live chat, and responding quickly and professionally to customer inquiries.
- Implement Fraud Prevention Measures: Use fraud detection tools and systems to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions. This can include using address verification services, card security codes, and IP geolocation tools to help verify the identity of customers and prevent unauthorized transactions.
- Provide Clear and Concise Product Descriptions on Billing Statements: Ensure that your customers understand the products or services they are being billed for by providing detailed and concise descriptions on their billing statements. This can reduce confusion and help prevent chargebacks resulting from customers not recognizing a charge.
- Offer Customer-Friendly Return Policies: Make it easy for customers to return products or cancel services if unsatisfied. This can include offering a no-questions-asked return policy or providing flexible cancellation options.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Chargeback Rate
- Subscription Plan: Tracking chargeback rates by subscription plan can provide insights into whether specific products or services have higher chargeback rates, which could indicate the quality or customer satisfaction issues.
- Customer Demographic: Tracking chargeback rates by customer demographics, such as age or location, can provide insights into whether certain groups of customers have higher chargeback rates, which could indicate issues with marketing or customer experience.
- Card Network: Tracking chargeback rates by card network can provide insights into whether specific payment methods or card networks have higher chargeback rates, which could indicate fraud prevention or payment processing issues. This will also help you track your compliance with card network-specific thresholds.
- Geographic Location: Tracking chargeback rates by geographic location can provide insights into whether certain regions have higher chargeback rates, which could indicate fraud or product delivery issues.
By segmenting data, you can gain a more comprehensive and actionable understanding of chargeback rates, which can help you reduce chargebacks, protect your bottom line, and improve your reputation with customers and card networks.
Fraud Detection Rate
Definition of Fraud Detection Rate
Fraud detection rate represents the number of attempted fraudulent transactions that are successfully caught and prevented.
Importance of Tracking Fraud Detection Rate
By closely monitoring your fraud detection rate, you can identify and respond to changes in the level of fraud risk. A high fraud detection rate indicates that your business effectively catches and prevents fraudulent transactions. In contrast, a low rate may reveal gaps in your fraud prevention measures that need to be addressed.
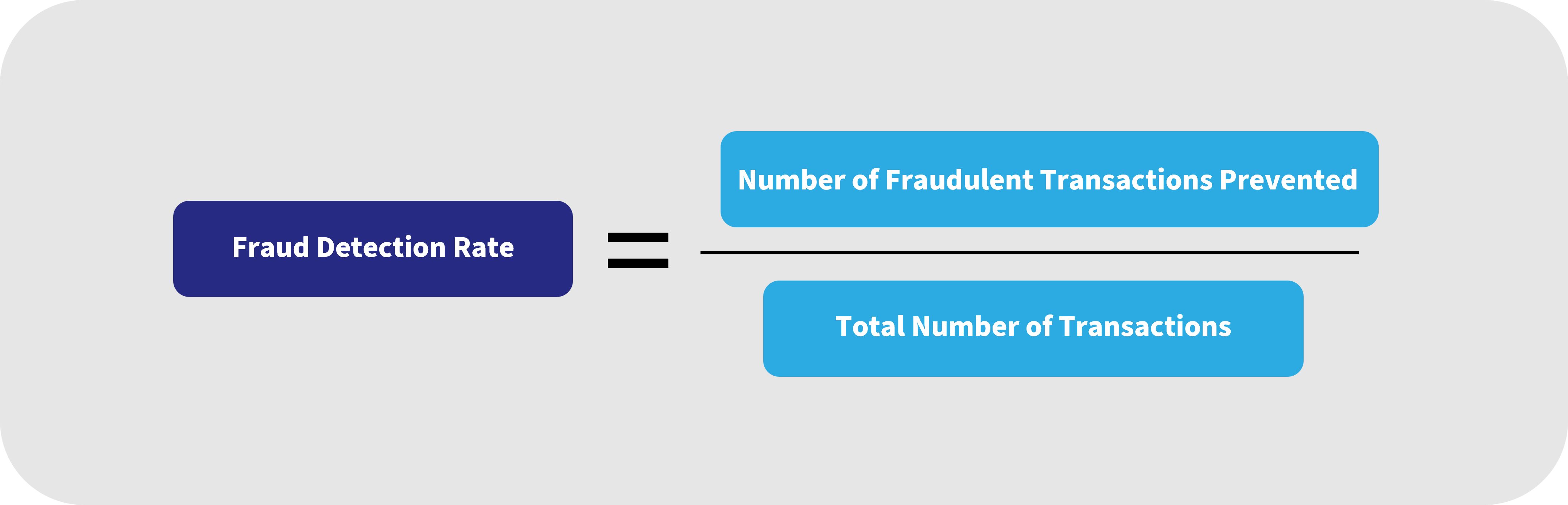
How to Calculate Fraud Detection Rate:
The fraud detection rate is calculated as the number of fraud attempts that are prevented divided by the total number of transactions, including both successful and unsuccessful attempts.
Strategies for Reducing Fraud Detection Rate:
- Use Multi-Layered Fraud Detection: Utilize a combination of machine learning algorithms and rule-based systems to improve fraud detection accuracy and prevent fraudulent activities, resulting in lower losses due to fraud and reduced chargebacks.
- Analyze Customer Behavior and Purchase History: Analyze customer data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate fraudulent activities. This approach can help improve fraud detection accuracy, reduce the number of fraudulent transactions, and gain a better understanding of customer behavior.
- Monitor Industry Trends and Best Practices and Implement Strategically: Regularly review and implement new tools and techniques to combat and stay ahead of new types of fraud and detection methods.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Fraud Detection Rate
- Transaction Type: Segment by transaction types, such as online or in-store purchases, to understand the fraud trends specific to each type of transaction.
- Payment Method: Segment by payment methods, such as credit card or PayPal, to identify any correlation between payment method and the likelihood of fraudulent transactions.
- Geographic Location: Segment by geographic location to identify regional fraud trends and potential areas where fraud prevention measures can be improved.
- Customer Behavior: Segment by customer behavior, such as purchase history and frequency, to identify patterns or correlations that may help prevent fraudulent transactions.
Data segmentation is a critical component of effective fraud prevention and management. This helps you make informed decisions about allocating resources for fraud prevention and ensures that your measures are targeted and effective.
Account Updater Rate
Definition of Account Updater Rate
Account updater rate is the success rate of an automated service that updates the information on file for your customer’s credit card, such as the expiration date or updated account number. This service minimizes the impact of expired or lost credit cards on your subscription billing.
Importance of Tracking Account Updater Rate
It is crucial to keep credit card information up to date to avoid failed transactions and revenue loss. By monitoring the success rate of the account updater service, you can understand the reliability of your payment process and identify areas for improvement.
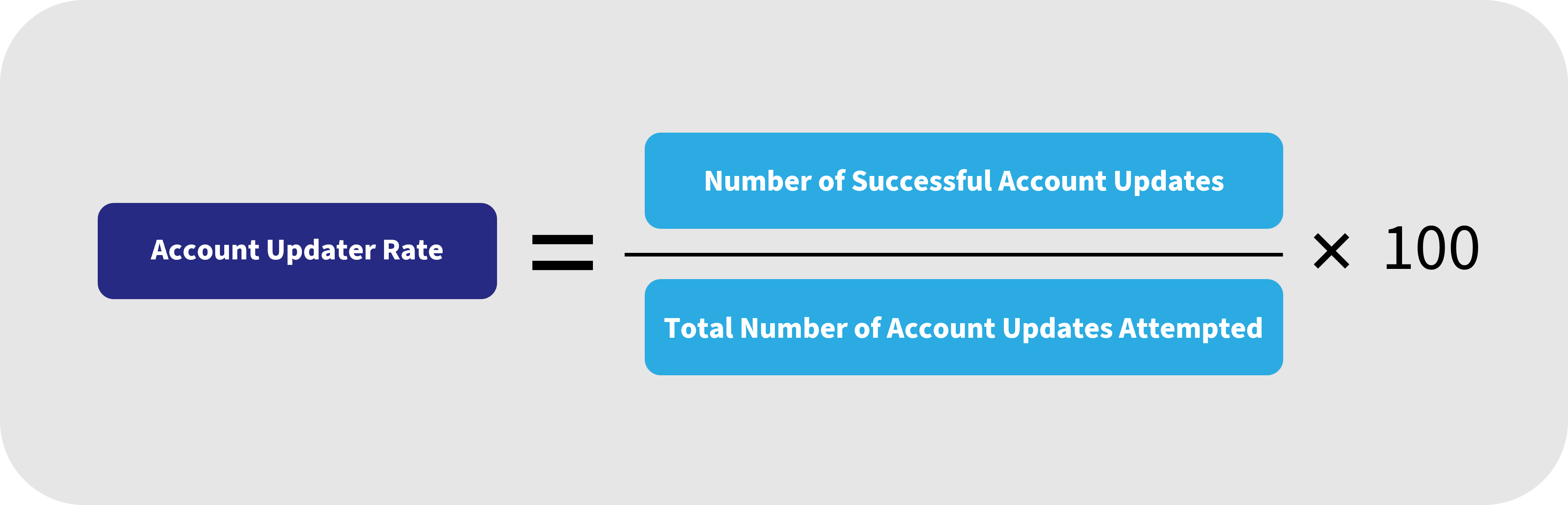
How to Calculate Account Updater Rate
You can calculate the Account Updater Rate as the number of successful updates divided by the total number of updates attempted, expressed as a percentage.
Strategies for Improving Account Updater Rate
- Use a Reliable Payment Gateway: Implement a reliable payment gateway with a high success rate for account updater services.
- Optimize Account Update Requests: Aim to update customer payment information at the most appropriate time, often when the customer’s billing cycle is about to be renewed.
- Utilize Real-Time Account Updates: Use payment processors that offer real-time updates, which can ensure that the payment information is up to date at the time of the transaction.
Examples of Data Segmentation Considerations for Account Updater Rate
- Response Code: Analyze the success rate of updates based on the specific response codes received from the account updater service. This can help you understand which updates will likely fail and adjust your process accordingly.
- Bank Identification Number (BIN) Range: Segment updates based on the bank that issued the credit card to understand any trends or patterns in the success rate of updates from specific banks. This can help you identify any issues with specific banks or payment providers and make changes to improve the success rate of updates.
- Customer Type: Segment updates based on the type of customer, such as business or consumer, to understand any differences in the success rate of updates for different customer segments. This can help you identify any customer communication or process issues that may impact the success rate of updates for specific customer types.
Data segmentation helps you understand the key drivers of your account updater rate, such as the success rate of updates from specific banks or specific customer segments or the timing in which updates are requested and processed. By analyzing this information, you can identify areas for improvement and update the processes to increase the success rate of updates and minimize the impact of expired or lost credit cards on your customers and bottom line.
Conclusion
Tracking each of these billing and payment-related metrics will provide unique insight into the performance and health of your billing and payment processes, helping you identify areas for improvement.
Remember that data segmentation is essential to tracking these metrics, as it provides a more granular understanding of the different components contributing to the overall performance. By analyzing the data segmented by other criteria for each metric, you can better understand the root cause of any issues and target specific areas for improvement.
Ultimately, tracking these metrics and taking a data-driven approach to improving billing and payment processes can increase customer satisfaction, reduce friction, and lower costs.
For more information on how to track and optimize your subscription billing metrics or to speak with an expert in the field, please contact info@rebartechnology.com. Whether you want to start tracking your metrics or need help analyzing and optimizing your existing data, we are here to help you succeed.

